Navigating the world of SEO can sometimes feel like you’re trying to learn a whole new language. One where the backlinks link back until you hit back and back track to where the backlink’s at. But don’t worry, we know where it’s at and we’ve got your back. We’re here to be your trusty translators.
This guide on SEO terminology is designed to break down the jargon and make SEO a whole lot less intimidating.
Whether you’ve been one of our SEO clients for years, or you’ve just started dipping your toe into the waters of SEO, this guide is designed to clarify the key concepts and phrases you’ll come across.
From ‘backlinks’ to ‘white hat SEO’, ‘bots’ to ‘domain authority’, we’ve got you covered.
Before we begin though, we’d like you to remember, there’s no such thing as a silly question. Feel free to ask us if you’ve got any queries (SEO pun 100% intended) about any of the terms we’ve covered here, or anything else you come across. At Excite Media, we’re always here to help.
So without further ado, let’s decode some SEO terminology.
We’ve sorted these into general categories, to make everything easier to understand, but a few of these will apply to a few different categories.
Table of Contents
ToggleGeneral Terms
SEO
SEO stands for search engine optimisation. It means essentially making sure that your website is geared to perform as well as it can in the organic search engines.
Search Engines
We’re pretty sure you’ve heard of these. They’re the platforms people use to search for things on the internet, like Google and Bing. Google is still the most popular, so we’ll refer to it the most in this article, however many things that are true for one search engine, are true for all.
SERP
Stands for “Search Engine Results Page”. It’s the page of search results that you see after you search for something on Google or other search engines.
Organic
The word organic refers to natural, non-paid visibility in search results. Organic rankings are achieved through SEO (Search Engine Optimisation).
Organic traffic is the website traffic you’ve gained outside of paid ads. Sometimes organic search traffic will be referred to as simply ‘organic’ as a kind of shorthand, but ‘organic’ can be anything that’s not paid ads.
Search terms/phrases/keywords/queries
These are the words or phrases that people enter into search engines like Google, when they’re searching for something.
When we say ‘keywords’ we don’t just mean one word (although it can be a word). It’s usually a phrase. Search terms, search phrases and keywords really just mean the same thing, when it comes to SEO.
Technically speaking, a search term is a word, a keyword is a word, and a phrase is well, a phrase, but these days these are all used interchangeably to mean the same thing, especially in the world of SEO. Technically a search query is a question that is searched in a search engine, but it is also often used interchangeably.
SEO optimising is all about ensuring that your website is geared to perform well for specific keywords/search terms/search phrases that are relevant to your offering and that are searched for by people looking for what you offer.
Long Tail keywords
Long Tail keywords are specific and detailed phrases that people use in search engines. Unlike broader, more general keywords, these are quite specific and often longer — hence the name ‘long tail’.
Broad keywords
Broad keywords are, well, broader! They can be very broad, and as a result, much harder to rank for than long tail keywords.
An example of broad keywords vs long tail keywords for the topic of shoes, a very broad keyword would be ‘shoes’, or ‘running shoes’. A long tail keyword would be ‘women’s red running shoes size 7’.
Keyword research
Keyword research is an important part of your SEO strategy, and one of the first things we’ll do.
It involves identifying and researching the words and phrases that potential customers use when searching for your product or service. During this process, we’ll look at the different things people search for, how often they search for specific terms over others, and how much competition there is for certain keywords and search terms. We also look at the value of different search terms. This lets us know what keywords we can/could/should focus on to get you the maximum results and increase your visibility in search results for relevant terms. Of course, relevancy and ‘search intent’ also comes into play here as well.
It sounds simple, but takes a fair bit of expertise, and takes a bit of doing to do right.







Relevancy
Relevancy in the world of SEO refers to how relevant your website and content is to the search term that people are entering into Google.
It also relates to how relevant a particular search is to you.
For example, when we do your keyword research, we’ll consider not just how often certain search terms are searched for on Google, but also whether those terms are relevant to you. After all, there’s no use ranking for Girl Scout Cookies if you are a car mechanic that has nothing to do with cookies.
Intent
Search intent is about understanding what a user is really looking for when they type in a search query. We take this into account when optimising your site, making sure your pages not only use the right keywords, but also deliver the information or services your potential customers are seeking.
For example, someone searching for “chocolate chip cookies” are most likely intending to find results for cookies of the tasty bakery goods variety. Someone searching for “website cookies” is likely searching for information on website cookies that track user information for reporting purposes.
Intent is about what they’re looking for, and also looking into why they’re probably looking for this. Intent is usually broken down into two categories: informational and commercial.
Informational vs commercial search queries
When people use a search engine, they could be looking for information (“how to change a tyre”) or looking to buy something (“buy Mercedes tyres online”).
We’ll optimise your site to cater to both types of queries, making sure that whether your customers are in the research phase or ready to purchase, they’ll find you.
Commercial intent search queries are usually more valuable, and higher in competition, as they hold more purchase intent and therefore have more to gain from acquiring traffic for, than informational search queries.
Keyword difficulty
Keyword difficulty, sometimes also referred to as keyword competition, is a measure of how hard it would be to rank on the first page of search results for a particular keyword or phrase. When you’re optimising for a certain keyword, you’re competing against every other website that wants to rank for that keyword, or that mentions that keyword. Keywords with high difficulty are usually those with high competition and are harder to rank for.
It’s not that keywords with low difficulty are easy to rank for, but more that keywords with a higher keyword difficulty will take more effort (and usually more time) to rank well for. Those with a high difficulty score already have a lot of well-established and well-optimised websites ranking for those keywords. It can be tough for a new or less authoritative website to rank in those top spots for certain terms. We’ll consider the keyword difficulty of different search terms when we do your keyword research so that we can help get you some quicker wins, as well as going after the big money-making keywords for you.
Content research
Content research is research that looks into what content should be created for your website in order to perform best for SEO for certain keywords. Within your content research, we’ll create a content plan for you, which will look at what long-tail and query-based keywords and phrases we’ll target from a content standpoint, and what blogs should be created for your website to improve your SEO.
We use a bunch of tools and techniques to figure out what content needs to be created, what structure and format it needs to be, how long it should be, what questions it should answer, or subsections it should cover, what long-tail keywords and phrases we should target, and more.
We’ll look at things like what people search for, what your high-performing competitors are ranking for, and more, in order to plan out what content and topics for blog articles could see the best results for your website for SEO.
Bots/crawlers/web crawlers
Bots/crawlers/web crawlers all refer to the same thing: automated programs that search engines like Google use to scour the internet, looking at all the content they can find, in order to display relevant results to people when they search for something in Google. The information these bots gather helps the search engines understand what your site is about and how it should be ranked for particular search queries.
Bots or crawlers regularly search through the internet, and when they find you, they’ll take a look at the content on your website, external factors and technical factors, to determine how relevant you are for certain topics and keywords, and how much of a solution you will be to certain searches.
Black hat SEO
Black hat SEO is kind of like the ‘bad guy’ SEO. In old Western movies, the bad cowboys wore black hats, while the good guys wore white hats. The black hat term is based on that. It refers to SEO tactics designed to trick the search engines, in ways that are generally frowned upon and that go against the rules and terms of service of search engines. A lot of black hat SEO tactics are a poor user experience and are pretty risky. If you’re caught, you’re likely to be penalised.
Some things used to work ‘back in the old days’ of SEO — like hiding keywords in white text on a white background. Today, search engines can usually tell, and sites get penalised for this. They may see short-term gains, but they run high risks as well.
It’s important for us to mention here that we definitely don’t recommend black hat SEO techniques. Ever. We’ll personally never use these techniques at Excite Media, for us or for any of our clients, because the risk isn’t worth it. Also, it never pays off in the long-term.
White hat SEO
White hat SEO is the ‘good guy’ SEO. It’s SEO that is ethical and goes with the best practice and is within the approved terms of agreement of search engines. White hat SEO has lasting effects and includes techniques like improving user experience, using relevant keywords, and creating high-quality content.
Grey hat SEO
Grey hat SEO are tactics that combine the good tactics of white hat SEO, with the bad tactics of black hat SEO, or that push the boundaries of white hat SEO and are borderline black-hat, or very questionable. It’s a good idea to stay away from black hat SEO.
Competitors (in the context of search)
In the context of organic search marketing, competitors don’t necessarily refer to your business’s top competitors, but rather the top competitors for the keywords you’re targeting, or the most relevant keywords for your business.
These are other businesses that rank for the same keywords and topics that your website targets or ranks for. Understanding your search competitors can help you refine your SEO strategy.
UX/User Experience
This term refers to a user’s overall experience when interacting with a website. A positive user experience can improve your site’s SEO, as search engines prefer to direct users to sites that are user-friendly. (If they sent you to results that were a terrible experience, they’d be a terrible experience, and that would lose them users, and business — so UX is important).
Local SEO and the “local pack”
Local SEO is a branch of SEO that focuses on local search results, and location-based searches. This can include searches with geological qualifiers (like the city name or suburb name), ‘near me’ searches, and searches by people in your local area.
The main goal of local SEO is to get your business to appear in the “local pack”, which refers to the top three spots on Google Maps. They’re super hot commodities because they’re seen by people in the local area searching for relevant things, and this closeness usually indicates pretty high intent to purchase/visit/interact right then and there.
SEO Tools
Google Alerts
Google Alerts is a web monitoring tool which can be set up to notify you when it finds new results that match your saved search terms. They can be used to monitor your online presence or keep an eye on what’s being said about certain topics.
Ahrefs
This is a toolset for SEO and marketing. It includes tools for backlink research, organic traffic research, keyword research, content marketing & more. It’s one of the tools we use for your SEO.
Google Search Console
Google’s Search Console is a tool we use to understand how your website is performing in Google search results and identify any potential issues.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is the free tracking and reporting platform for your website, provided by Google. You’ll need the tracking codes set up on your website to begin. Google Analytics can give you a huge amount of insight into your website visitors, their behaviours, and how they found their website. It can help to fine-tune your SEO strategy. If you’re a client with us, we’ll help you get set up with Google Analytics at the start of the process, if you haven’t got it already.
Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager is a Google tool that helps manage your tracking tags (which are snippets of code on your website that help you track and report). It means that you can update your tracking without having to modify the code on your website. This is useful for SEO as it allows easy implementation of SEO-related features, such as event tracking and schema markup. If you are a client with us, we can help you with Google Tag Manager.
Google Business Profile (GBP)
Google Business Profile was formerly known as Google My Business (GMB). It’s also known commonly as a ‘Google Maps listing’. This is a free tool that lets you manage how your local business appears on Google Search and Google Maps. Managing and optimising your Google Business Profile is a part of local SEO (location-based SEO) and can help improve your overall SEO.
On-page SEO terms
On-page SEO refers to the SEO optimisations that happen on your website’s pages, they’re changes to the actual content.
Page Titles, Meta Descriptions and Metas/Metadata
These are all parts of a webpage that tell search engines and users what your webpage is about. Webpage meta descriptions, and page titles, are both ‘meta data’ or ‘metas’. A page title is, a title for your page, and shows up in the top internet tab, as well as in the title of the search result that you see come up in the search engine results page. A meta description is a short blurb that summarises what the page is about, and it’s what you see under the title in the search engine results page.
A well-optimised title and meta description can improve your click-through rates from search engine results pages, helping to drive more traffic to your site.
Alt tags/Image alt text
Alt tags, also referred to as image alt text, are a brief description of each of the images on your webpage. They help to explain to search engines, and to people with accessibility needs, what the images are about. Image alt text can also help your website become visible in image searches, adding another avenue for potential customers to find you.
Internal linking
Internal linking is when we link from one page on your website to another. It helps users navigate your site and find related content, while also helping search engines understand the structure of your website and what pages are most important. The words that you use for these internal links are important, as they can also help with the SEO for particular keywords (they tell website crawlers what the link is about).
Keyword cannibalisation
Keyword cannibalisation isn’t good. It occurs when multiple pages on your site are targeting the same keyword, which can lead search engines to struggle to identify the most relevant page. It essentially means that you’re competing against yourself with two pages, instead of targeting different keywords on each page. We avoid this by ensuring each page targets a unique set of keywords, and mapping out a keyword strategy that sees the most relevant pages target each set of keywords.
Keyword stuffing
Keyword stuffing is an old SEO tactic that used to work but now will more likely see you drop in rankings. It involved overusing a keyword (or multiple keywords) throughout a webpage in an attempt to manipulate search rankings.
You’ve probably come across it on the internet, and if you have, you can probably attest to it being a bad user experience. It impacts readability, credibility and search engine rankings.
It’s important to keep in mind that if you overuse keywords, you run the risk of being marked down for ‘keyword stuffing’. So we focus on creating natural, high-quality content that uses keywords appropriately, and only when they work and make sense.
Keyword stuffing is common in Google Business Profile (GBP) titles, but actually goes against Google’s guidelines, and you can have your business profile removed for this. We definitely don’t recommend keyword stuffing, ever — especially on GBP profiles, as they can be flagged by competitors.
Keyword frequency
This refers to the number of times a keyword or phrase appears on a webpage. We make sure to use your keywords naturally and appropriately, maintaining a good balance. Too many keyword references compared to the number of words on the page will probably get you flagged for keyword stuffing.
Heading structures
A well-structured page uses different levels of headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to organise content. This makes your pages easier to read for visitors and helps search engines understand the content better.
Readability
This measures how easy it is for people to understand your content. We aim for high readability, which means using clear language and structure to make your pages accessible to as wide an audience as possible. Google takes the structure of your content into consideration to determine how readable your content seems, and uses this to form part of its assessment of the user experience your site provides.
Copywriting
Copywriting basically means “writing the words” in marketing. If we refer to copywriting for your SEO, it will probably be in the context of content-based SEO optimisations. The content on your website plays a large part of your SEO, so there will most likely be some wording (copy) that needs to be written, edited, optimised or expanded on within your SEO efforts.
Schema Markup
Schema markups are also known as Schema.org or structured data. It’s a kind of code that uses structured language that helps search engines to understand and read your website and its content.
It’s a type of metadata that is more in-depth than your page title and meta description, as it provides context and helpful information.
For example, websites that list recipes, might use schema markup to specify things like cooking time, ingredients, and calories in a certain recipe. For websites that sell products, schema markups can list the product price, average customer rating and more. For event pages, the schema markup can show dates, locations and ticket availability. All of this information that the schema tells the search engines can mean that this information can be displayed on the Search Engine Results Page before the user even clicks through to your website.
Rich snippets
Good Schema Markups can make your organic search engine listings more visible and more attractive to website users. When schema markups result in extra information being shown in your search engine result on the search engine results page, it’s called a ‘rich snippet’,
Schema Markups are pretty technical and take ‘a bit of doing’ but can really improve your visibility and how you look in search engine results.
Technical SEO
These are the more technical elements of your SEO optimisation.
Index/indexing
This one can be a little tricky to explain, but think of it kind of like a contents list, or address book of every single website and webpage on the internet that’s relevant to a particular topic.
Indexing is the process that search engines (or their bots/crawlers) use to store and organise the content they find during their website crawling.
When a page is in the index, it’s been put on the list and is ‘in the running’ to be displayed as a result for relevant search queries.
Not every page will be indexed. But there are things you can do to make sure that your most important pages are indexed.
Shortened URLs
These are abbreviated versions of a website’s URL (web address). In SEO, it’s better if your URLs are clear and descriptive, and sometimes shortening a URL can make it more user-friendly. Updating the URL slugs can also make a URL more user-friendly. Be careful though — if you don’t know what you’re doing, going in and changing all your URLS can cause a world of issues with broken links and whatnot (we’ll cover broken links shortly). It’s best left to the experts.
URL Slugs
A URL slug is the part of the URL that identifies the particular page on a website in easy-to-read form. It’s the part of the URL that explains what the page content is.
For example, on a made up website, for a made up link www.megacoolwebsite.com.au/greatest-seo-blog-about-slugs,
The ‘greatest-seo-blog’ part is the slug and it tells you what the page is about — it’s an SEO blog about slugs.
Slugs help users, and bots, tell what your page is about before clicking through. It’s best-practice to keep these readable and clear, and to follow a similar url path structure across your website.
Page speed
This measures how quickly your webpage loads. A faster page provides a better user experience, which is an important factor for SEO as Google uses page speed in its ranking algorithm. If your page takes too long to load, people will ‘bounce’ (leave the page without interaction) due to poor user experience. So you want a good page speed.
Mobile friendliness
This refers to the design and functionality of your website on mobile devices. With a higher number of mobile web visits than desktop website visits on the internet overall, (and for most websites individually) it’s important to have a mobile friendly website, for user experience.
Importantly, Google indexes mobile-first, (meaning that they use the mobile version of a webpage first when they index a site), so it’s particularly essential for SEO. A poor mobile experience is just not okay on the internet these days — and your SEO is sure to suffer if it is sub-standard
Technical audit
This is a comprehensive checkup we perform to identify any technical problems that might be hurting your website’s performance in search engines.
Broken links
Broken links are pretty much the same as a 404. They’re essentially a link that doesn’t work, and this is a bad user experience and bad for SEO. So we find and fix these.
Robots.txt
This is a file that tells search engine bots which parts of your website they should and shouldn’t ‘crawl’ (read). It’s a bit technical and needs to be written correctly to ensure it doesn’t cause any problems.
Core website vitals/core vitals
These are a set of factors Google considers important in a webpage’s overall user experience, including loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. The core web vitals report in Search Console tells us how these factors are performing for your website. Core web vitals impact on your website’s SEO, because they impact on your user experience.
The current three main website core vitals are:
👉 Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
👉 First Input Delay (FID)
👉 Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Let’s look at a brief explanation of each, next:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
This measures the time it takes for the largest element on a webpage (like a video or image) to fully load and be visible to the user.
First Input Delay (FID)
This measures the time from when a user first interacts with a web page (like clicking a button or a link) to when the browser actually starts processing that interaction. FID is going to be replaced by a new core web vital, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) from March 2024. We’ve written a blog about this change — check it out here.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
This measures how much unexpected movement happens on a webpage as it loads, to measure the visual stability and if there are any annoying experiences for users in this area.
Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
This measures the time from when a user first interacts with a web page (like clicking a button or a link) to when the browser actually starts processing that interaction. FID is going to be replaced by a new core web vital, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) from March 2024. We’ve written a blog about this change — check it out here.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap (or sitemap.xml) is like a roadmap of your website that helps search engines find, crawl and understand what content is on your site. It can also identify what the most important pages to ‘index’ are on your site.
Site speed
This is a measure of how quickly users can see and interact with your content. A faster site can lead to better user engagement, more pages viewed, and improved rankings in search results.
Index bloat
Index bloat is what happens when search engines have indexed too many low-value pages from your website, which can dilute your overall domain authority and impact on your user experience. It’s something that we’ll look for, and work to fix, in some of our more technical SEO actions for your website.
404
When you go to visit a webpage or follow a link, a ‘404’ message and code, or ‘response’ might pop up. This is the code for “Page Not Found”. If a user or search engine bot tries to access a page that doesn’t exist, they’ll get a 404 error. We work to minimise these on your site, because they impact your SEO score negatively.
Health score
This is a general measure of your website’s technical health, including factors like page speed, error pages, and more.
Root directory
This is the top-level directory that contains all the files of your website on a server. Think of it as the “home base” for your website on your server. In terms of SEO, the important thing to know is that your root directory will contain your sitemap.xml file and your robotx.txt file, which can allow or restrict the crawlers and robots, assist them, give them directions, or give them some rules for crawling and indexing your site.
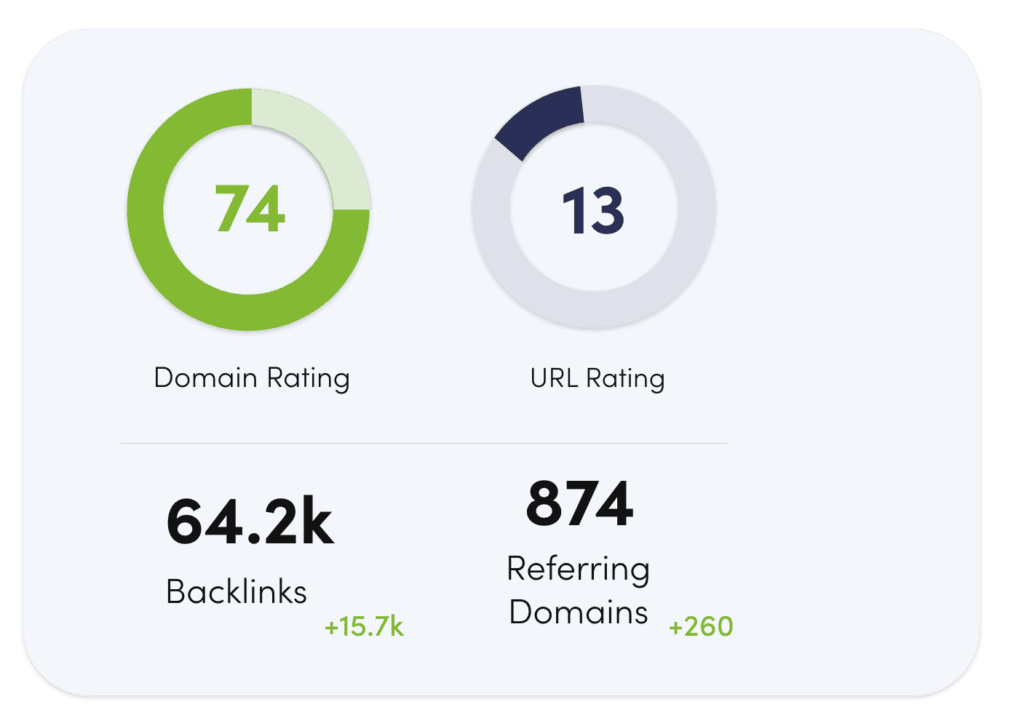
Linking/Off-Page SEO
Backlinks/inbound links/incoming links
These are links from other websites that point to your website. Think of them as votes of confidence from other sites that can help boost your site’s authority and visibility in search engines. If high-quality websites link to you, they pass on what is known in our industry as ‘link juice’ and you benefit from it. A lot of off-page SEO is based around getting good quality, relevant backlinks from trusted sites with good ‘authority’. But more on that shortly.
Follow links/do-follow
These are normal hyperlinks that allow search engines to ‘follow them’ and pass on ranking power to your website. If you link to another site on a blog, and it’s a ‘follow link’ or ‘do-follow’ link, it tells Google that you think that site is good value. So when a backlink that links to your website is a do-follow link, it passes on some ‘link juice’ (ranking power) to you.
No-follow links
These are links that tell search engines not to follow them or pass ranking power to your website, but they can still bring in valuable traffic. If you’re linking to a site but don’t want Google to see it as a vote of confidence, use a no-follow link. No-follow backlinks coming to you aren’t as good as they don’t give you the same ranking power, but they still bring traffic.
Guest posts
Writing articles for other websites can be a good way to gain exposure and earn backlinks. As long as these are quality websites with good domain authority.
Citations/citation building
In the world of SEO, citations are online mentions of your business, usually for local SEO (location-based SEO). They help customers find you and can impact how you rank in local search results.
Citation audit
This is where we check all your online business listings to make sure they’re accurate and consistent and have the right location information on them (like your phone number, address, open hours, etc.) — and including your ‘NAP’ (Name, Address, Phone Number) — which brings us to our next definition.
NAP
NAP stands for Name, Address, and Phone number. In local SEO, maintaining consistent NAP information across all online platforms and directories is crucial.
When your business’s NAP information is consistently the same across the web, it sends positive signals to search engines about the legitimacy and relevancy of your business. This can improve your local search rankings. On the other hand, if search engines find inconsistent NAP information, they may not have confidence in the accuracy of the details, which could lead to lower rankings in local search results.
So, if local SEO is a focus for you, part of our SEO work will be making sure that your NAP is listed and consistent. It’s an essential part of local SEO strategy.
External linking
This is when you link from your website to another website. It’s a good practice to provide your visitors with useful information and references.
Domain authority/domain ranking/site authority
This is a score that predicts how well a website will rank on search engine result pages (SERPs). A high Domain Authority is associated with a greater ability to rank.
Domain Ranking is kind of like a popularity contest, based on how well you know your topic.
In this popularity contest, your website is judged not only on how many friends and votes (backlinks and referring websites) it has, but also on how knowledgeable ( content quality) and trustworthy (consistent and accurate information) it is on a given topic. Vote Excite Media #1 for class president, we say.
High-quality vs low quality or harmful backlinks/link profiles
A link profile is the makeup of backlinks to your site. High-quality backlinks can help your site’s rankings, while low-quality or harmful backlinks can hurt them.
The best backlinks to get are those from high-quality sites, with good domain authority, that are credible, and receive high traffic. Backlinks from relevant websites for your industry or topic are high quality backlinks to gain as well.
On the other hand, if you have a bunch of backlinks linking to you from dodgy sites, this can actually harm your SEO. Being associated with dodgy sites is not ideal, and Google and other search engines can see this as an indicator that you might be doing some dodgy black-hat SEO practices. Luckily though, you can ‘disavow’ links that could cause problems.
Disavowing links and disavow files
If you have harmful or low-quality links pointing to your site, we can tell Google to ignore them by creating a disavow file. It’s like saying, “We don’t want to be associated with these links.”

Reporting/Tracking/Metrics
Website traffic
This is the number of people who visit your website. More traffic often means more potential customers.
Traffic filters
These are settings you can apply in Google Analytics to exclude specific types of traffic data from your reports, such as internal traffic from your own company. Filtering allows for cleaner data interpretation.
Position/ranking/keyword ranking/organic ranking
Your position or ranking is where your site appears in the search engine results pages (SERPs) for a certain search term or keyword, organically (without paid ads).
When you search something on Google, the first result that’s not an ad, is ‘position one’. The first ten positions are on page one of Google. A featured snippet is in position zero, as it appears before the first organic search result (another reason featured snippets are so desirable to get)!
Higher rankings (those closer to one) mean more visibility, and the more likely people are to find you. If your position is one, on average, you’re showing up in first position for that search term. Of course, being in position #1 does not guarantee all of the traffic. But it usually does get the most traffic.
Some search terms or keywords are very broad. Some are very competitive. SEO is all about identifying which keywords you want to rank higher for, and then optimising for this. While we can’t all be in position one for every relevant keyword, SEO efforts are designed to make your website perform as high as it possibly can, for set keywords or search terms. You’ve got to be in it to win it, in the world of SEO.
CTR/Click through rate
This measures the number of people who click on a link (like your website in search results) compared to the total number of people who see the link.
Conversion rate/Conv Rate
A conversion is an action that you want people to do on your website. A conversion could be a lead (form fill out or enquiry), an eCommerce purchase, a sign-up to a newsletter or list, or a phone call.
A conversion rate is the percentage of visitors to your site who take a desired action, like making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
ROI (Return on Investment)
In the context of SEO, ROI measures the profitability of your SEO efforts by comparing the cost of your SEO strategy to the revenue generated from organic search traffic.
Keyword gap analysis
This is a strategy in SEO where you identify keywords you’re not currently ranking for, but your competitors are. By filling in these “gaps”, you can find new opportunities for website traffic.
Competitor analysis
This process involves identifying your main SEO competitors and analysing their SEO tactics. By understanding what’s working for them, you can identify strategies that could work for you too.
Featured snippets
Featured snippets are a feature of Google’s search results, designed to directly answer a user’s search query right on the results page, without them needing to click through to a website. Featured snippets are a highly sought-after spot in Google search results due to the visibility they offer, and the credibility they give you to internet users (it’s very authoritative to be the answer on the search results page to a certain question).
They’re selected by Google’s algorithms to provide an answer to a question typed into Google, right there on the search results page. They’re pulled by Google from the web page that it thinks gives the best answer to that question. So when you win a featured snippet, you know you’re doing something very right!
Featured snippets vs schema markups vs rich snippets
They sound similar but they’re not quite the same. Here’s how they’re related. Both featured snippets and rich snippets make your listing more visible and attractive on the search engine results page.
A rich snippet is different to a ‘featured snippet’ because it relies on using schema markup.
Schema markup is something we actively add to your website, where a featured snippet is selected automatically by Google from the content on your website.
However, schema markup can help your chances of getting a featured snippet, because it makes your content easier for search engines to understand.
Got questions?
These explanations are designed to be simple and user-friendly, but of course, each of these topics can go much deeper. If you need more detailed information on any of them, don’t hesitate to ask!




